Thangka Mural Line Drawing Based on Cross Dense Residual Architecture and Hard Pixel Balancing
Author(s):N. Wang, W. Wang and W. Hu
Published In:IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 48841-48850, 2021
Keywords:Image edge detection , Training , Feature extraction , Detectors , Learning systems , Semantics , Task analysis , Edge detection , hard pixel balancing , line drawings , Thangka
Cite:N. Wang, W. Wang and W. Hu, "Thangka Mural Line Drawing Based on Cross Dense Residual Architecture and Hard Pixel Balancing," in IEEE Access, vol. 9, pp. 48841-48850, 2021, doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3068199.
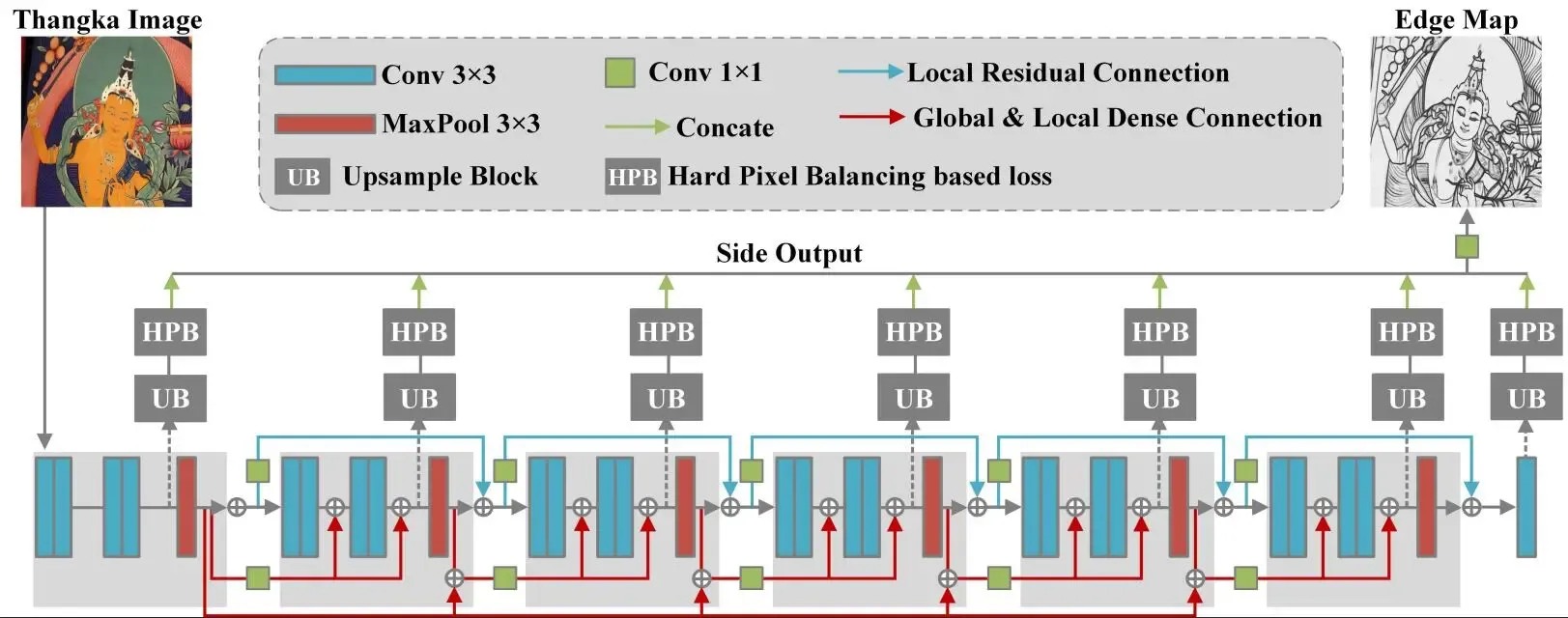
Thangka murals are precious cultural heritage for Tibetan history, literature, and art. Digital line drawing of Thangka murals plays a vital role not only as an abstracted expression of Thangka for art appreciation but also as a fundamental digital resource for Thangka protection. Digital Thangka line drawing can be categorized as image edge detection, which as a fundamental problem for computer vision, aims to extract visually salient edges from images. Varieties of high-level computer vision tasks depend on edge detection. Although existing non-learning and learning-based edge detection methods have progressed, they failed to generate semantically plausible thin edges, especially thin in-object edges. We propose a novel deep supervised edge detection solution Richer In-object Thin Edge Network (RITE-Net) to generate line drawings of Thangka mural images. Compared to existing studies, firstly a new Cross Dense Residual architecture (CDR) is proposed to propagate abundant edge features effectively from shallow layers to deep layers of CNN using a long-range feature memory; Secondly, a new Hard Pixel Balancing (HPB) based loss function strategy is designed to focus on hard pixel distinguishment. Experiments and tests on different datasets show that the proposed RITE-Net is able to produce more visually plausible and richer thin edge maps comparing to the existing methods. Both objective and subjective evaluations validated the competitive performance of our method.